Glossary
Association of Investment Companies (AIC)
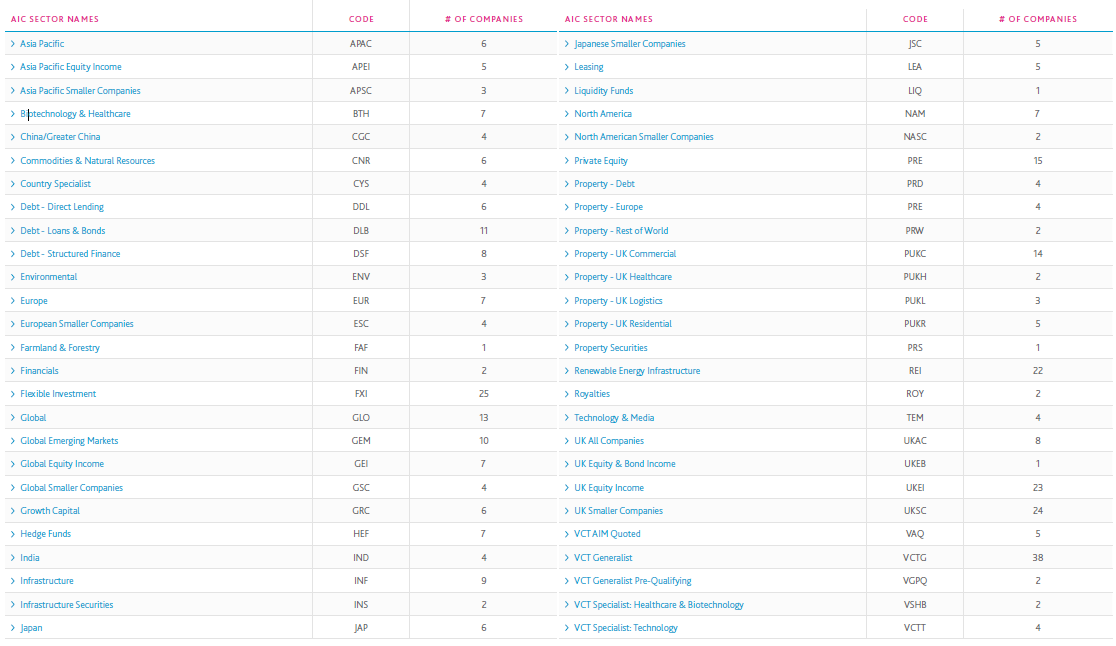
The AIC is a trade association that represents investment companies in the United Kingdom. Its members are investment companies and other closed-end funds that invest in a range of assets, including equities, fixed income, property, and alternative investments. The companies researched are all members of the AIC.CDP
CDP (formerly known as the Carbon Disclosure Project)
The CDP is a non-profit organisation that encourages companies and cities to disclose their environmental impacts and strategies for addressing climate change.
European Public Real Estate Association Sustainability Best Practice Recommendations (EPRA sBPR)
EPRA sBPR is a set of voluntary guidelines that provides a standardised framework for reporting sustainability performance in the real estate industry. The guidelines cover a range of ESG issues and promote continuous improvement in sustainability performance by encouraging companies to set targets and track progress over time.
Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark (GRESB)
GRESB is an organisation that assesses and benchmarks the sustainability performance of real estate portfolios and infrastructure assets globally. It provides a standardised framework for evaluating the sustainability of buildings and infrastructure.
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
GRI is an international independent standards organisation that helps businesses, governments, and other organisations understand and communicate their impacts on issues such as climate change, human rights and corruption.
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
SASB is an independent organisation that provides industry-specific sustainability accounting standards for use by publicly listed companies in disclosing material sustainability issues to investors. By providing a common language for reporting on sustainability issues, SASB aims to improve the quality and comparability of sustainability data.
Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)
SFDR is a European Union regulation that requires financial market participants and financial advisors to disclose how they integrate sustainability risks and factors into their investment decision-making processes. One of its purposes is to prevent so-called ‘greenwashing’ by ensuring that companies cannot falsify their ESG credentials. SFDR requires firms to be classified as either Article 6, Article 8 or Article 9:
- Article 6 relates to funds that have no sustainable objective and may include funds that invest in unsustainable products such as coal producers
- Article 8 relates to funds that promote ESG characteristics
- Article 9 relates to funds that have sustainable investment as their objective
SFDR does not apply to all companies as only firms with more than 500 employees and those that are based or market themselves in the EU are obligated to comply, but those with fewer than 500 employees must either comply or explain why they do not.
Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
TCFD is a global initiative established by the Financial Stability Board to develop voluntary, consistent climate-related financial risk disclosures for use by companies, banks, and investors. The TCFD framework provides guidance on how companies can disclose climate-related risks and opportunities in their financial filings. TCFD is mandatory for companies with more than 500 employees and a turnover of £500 million+.
United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (UNPRI)
UNPRI is a global network of investors committed to integrating ESG factors into their investment decision-making processes and ownership practices. The PRI framework provides a set of principles and best practices for investors to follow, which can help them align their investments with sustainable development goals and promote positive social and environmental outcomes. Signing the UNPRI is voluntary.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs)
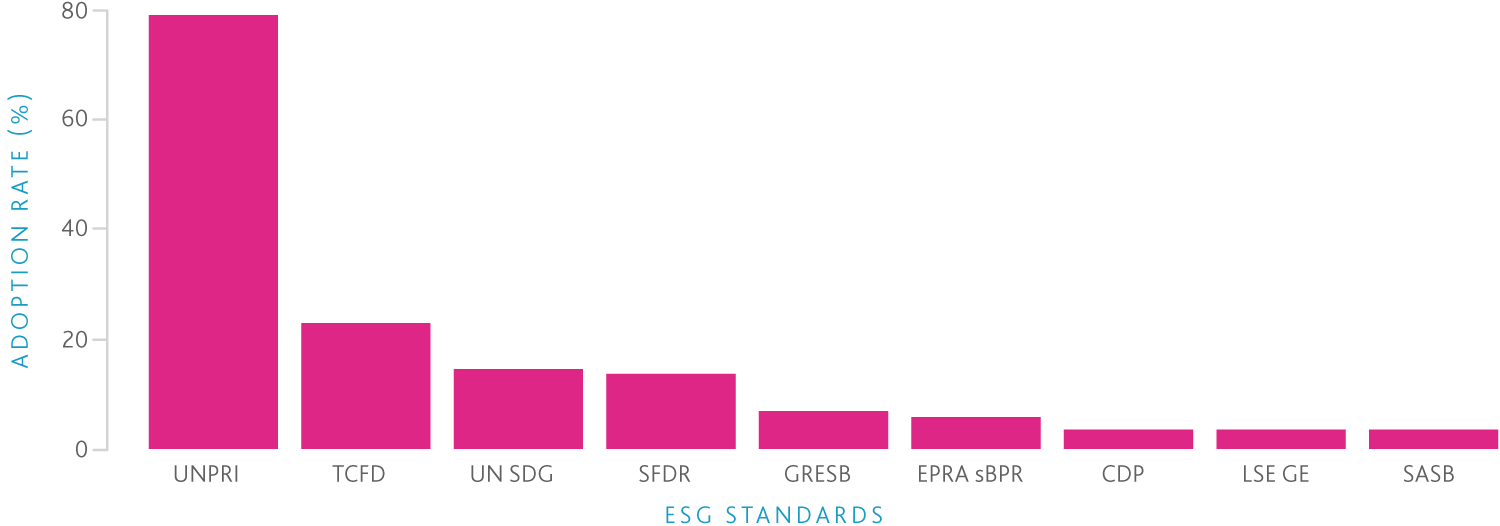
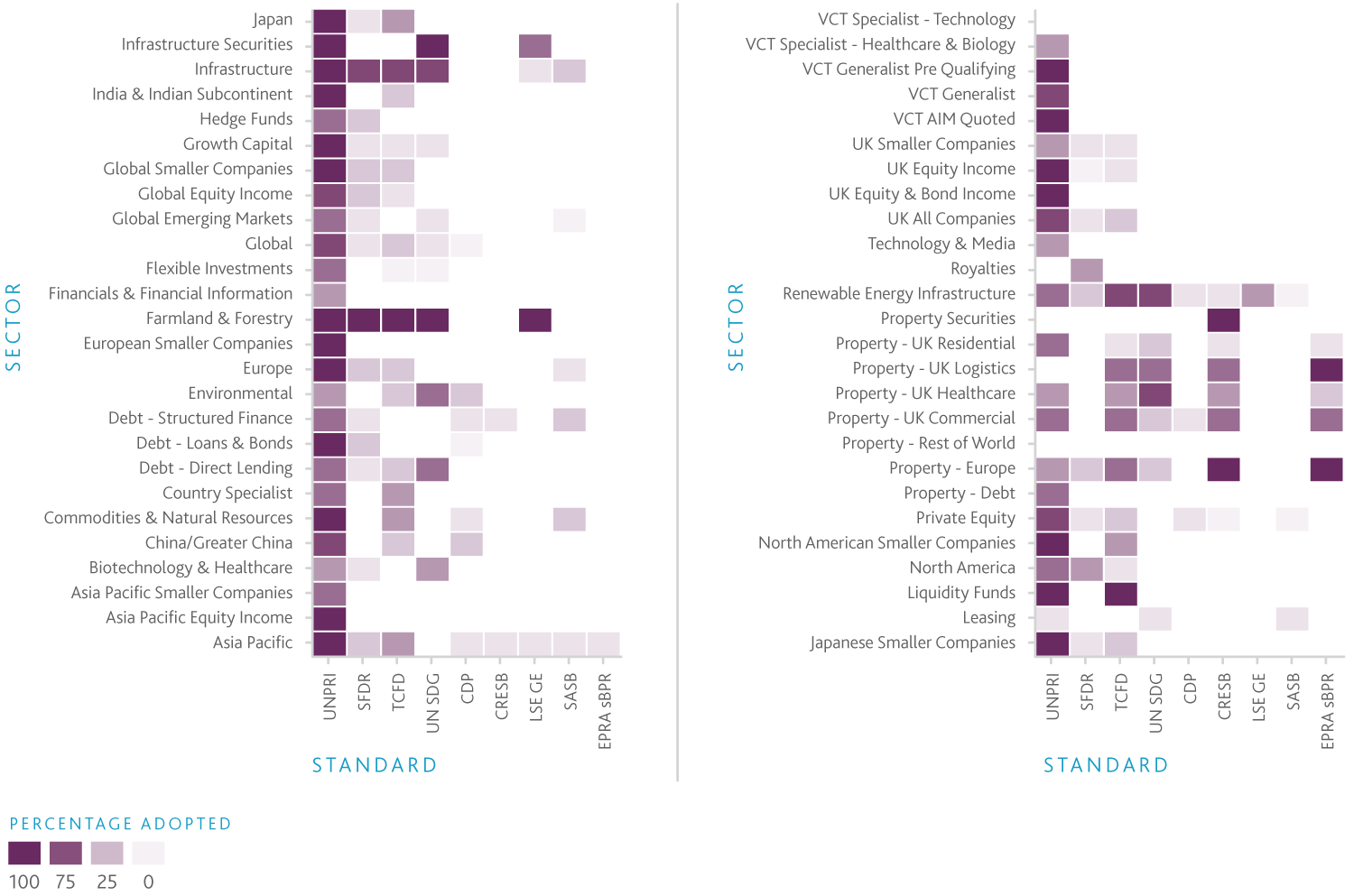
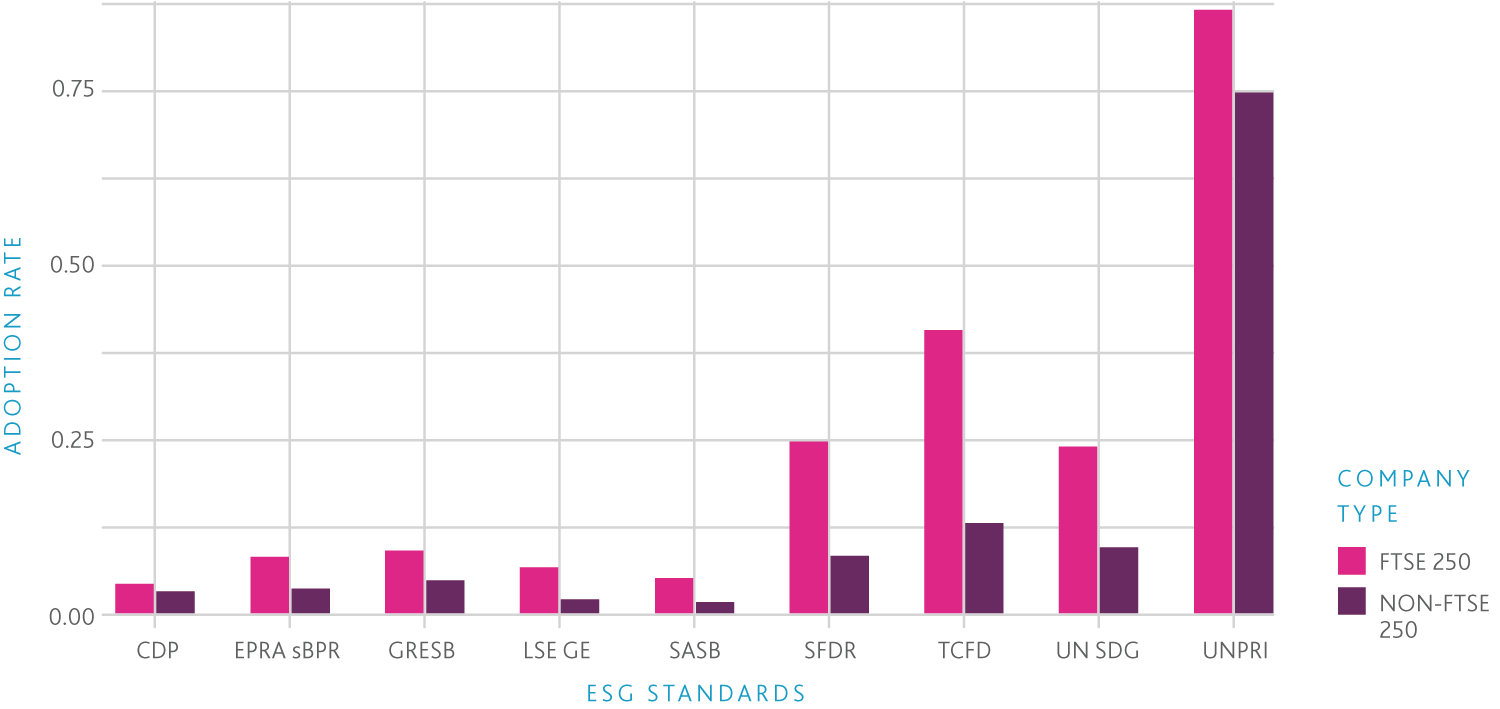
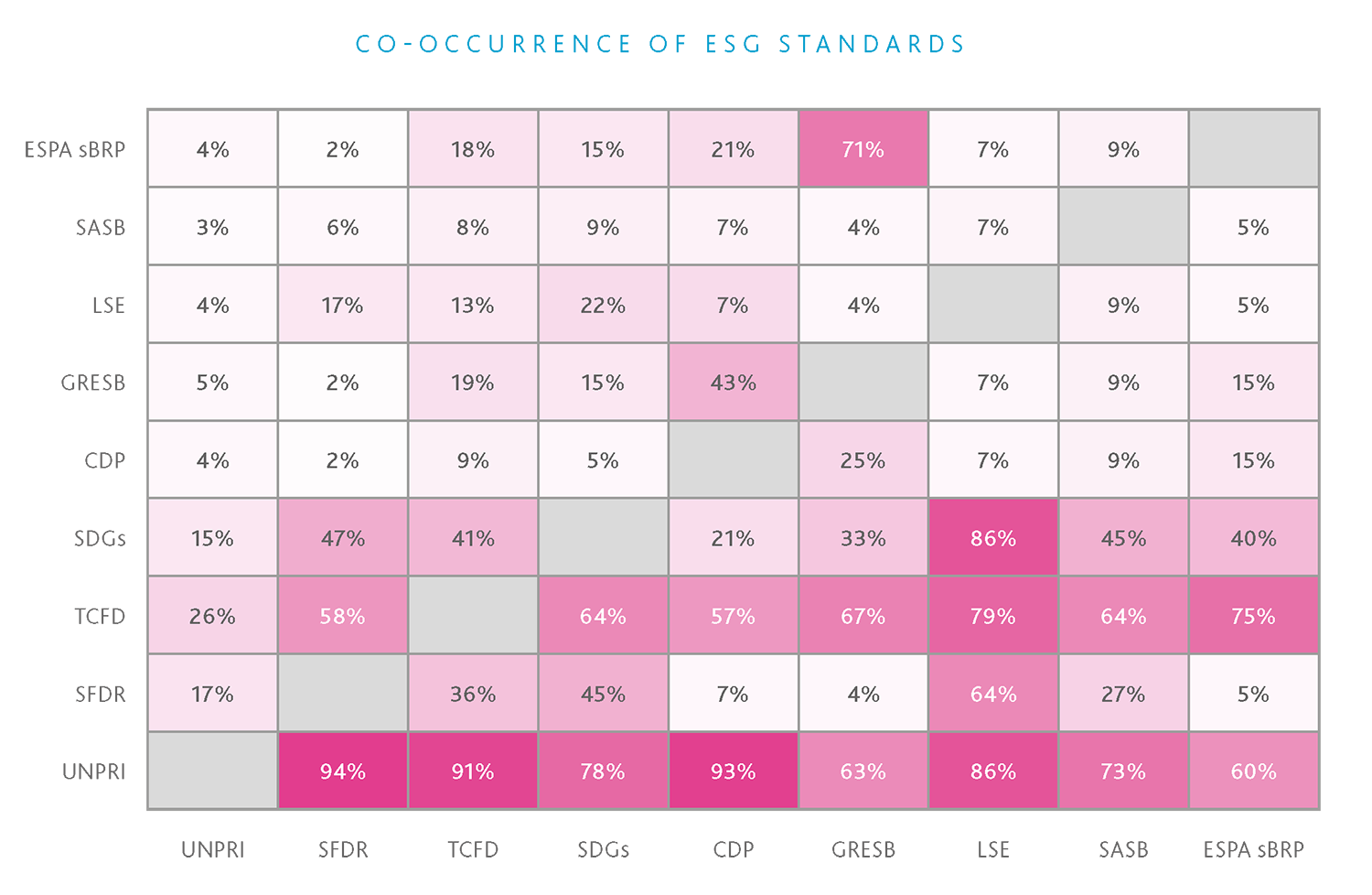
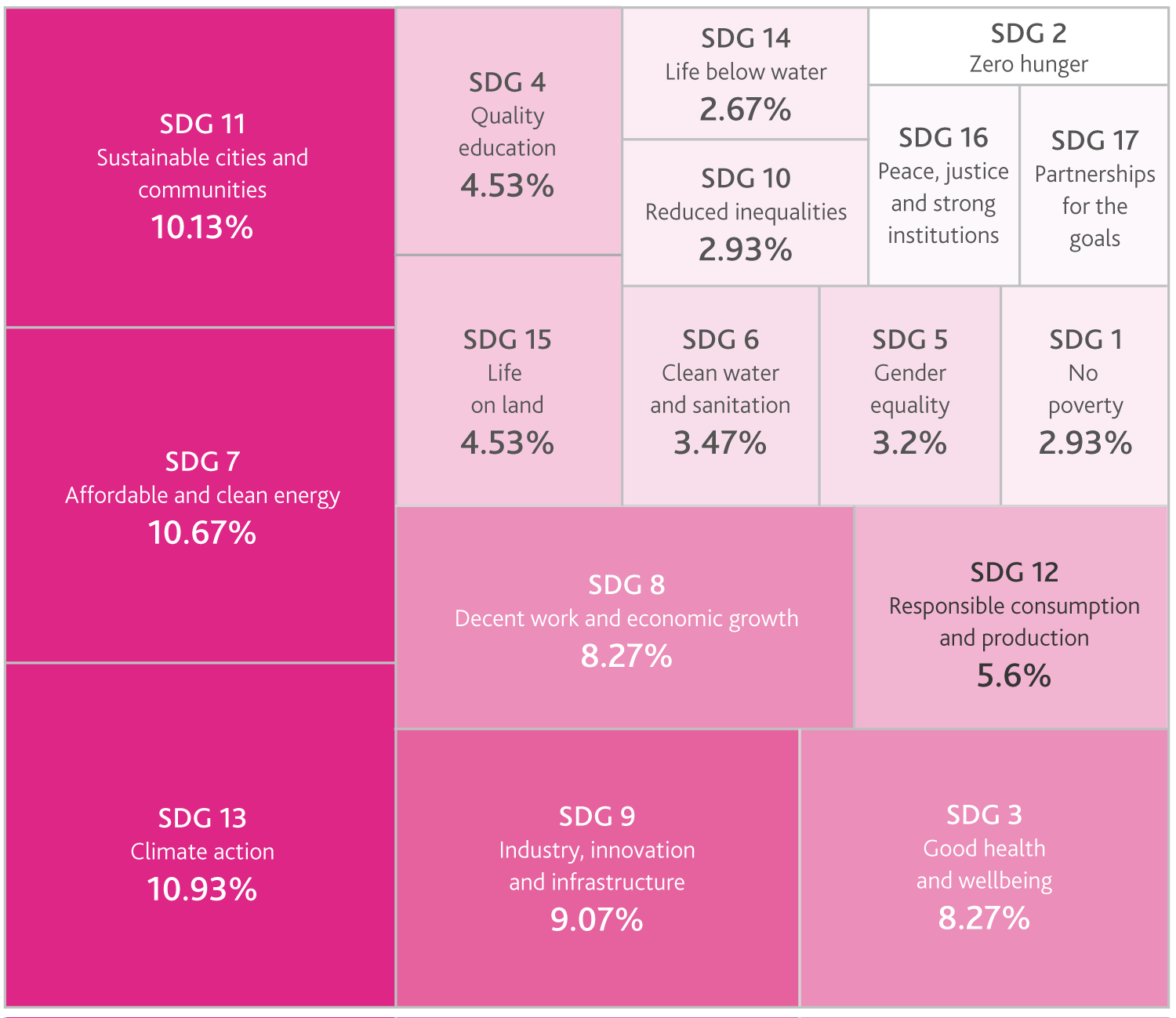
UNSDGs are 17 goals adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015 to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation by 2030. The SDGs provide a framework for governments, businesses, and civil society to work together on sustainability issues. There are many other ESG standards, though these are the most common among the investment companies researched. Additionally, when reference is made to an ESG ‘standard’, it is generally referring to one or all of these.